Table of Content
Did you know that coolant, also known as antifreeze, plays a crucial role in the automotive industry? Its importance lies in its ability to regulate engine temperature, prevent overheating, and protect vehicles against corrosion and rust.
You see, the internal combustion engine in a vehicle generates a tremendous amount of heat as it burns fuel to generate power. Without proper cooling, the engine would quickly overheat, causing extensive damage and potentially rendering the vehicle inoperable.
Coolant helps prevent overheating by absorbing and transferring heat from the engine to the radiator, where it is dissipated. Additionally, coolant contains additives that protect the engine and cooling system components from corrosion and rust.
These additives prevent the buildup of scale and deposits that can clog the radiator and cooling system passages, reducing coolant flow and increasing the risk of overheating. Therefore, using the correct type of coolant is critical in the automotive industry. Using the wrong type of coolant can cause chemical reactions that damage engine components and result in costly repairs.
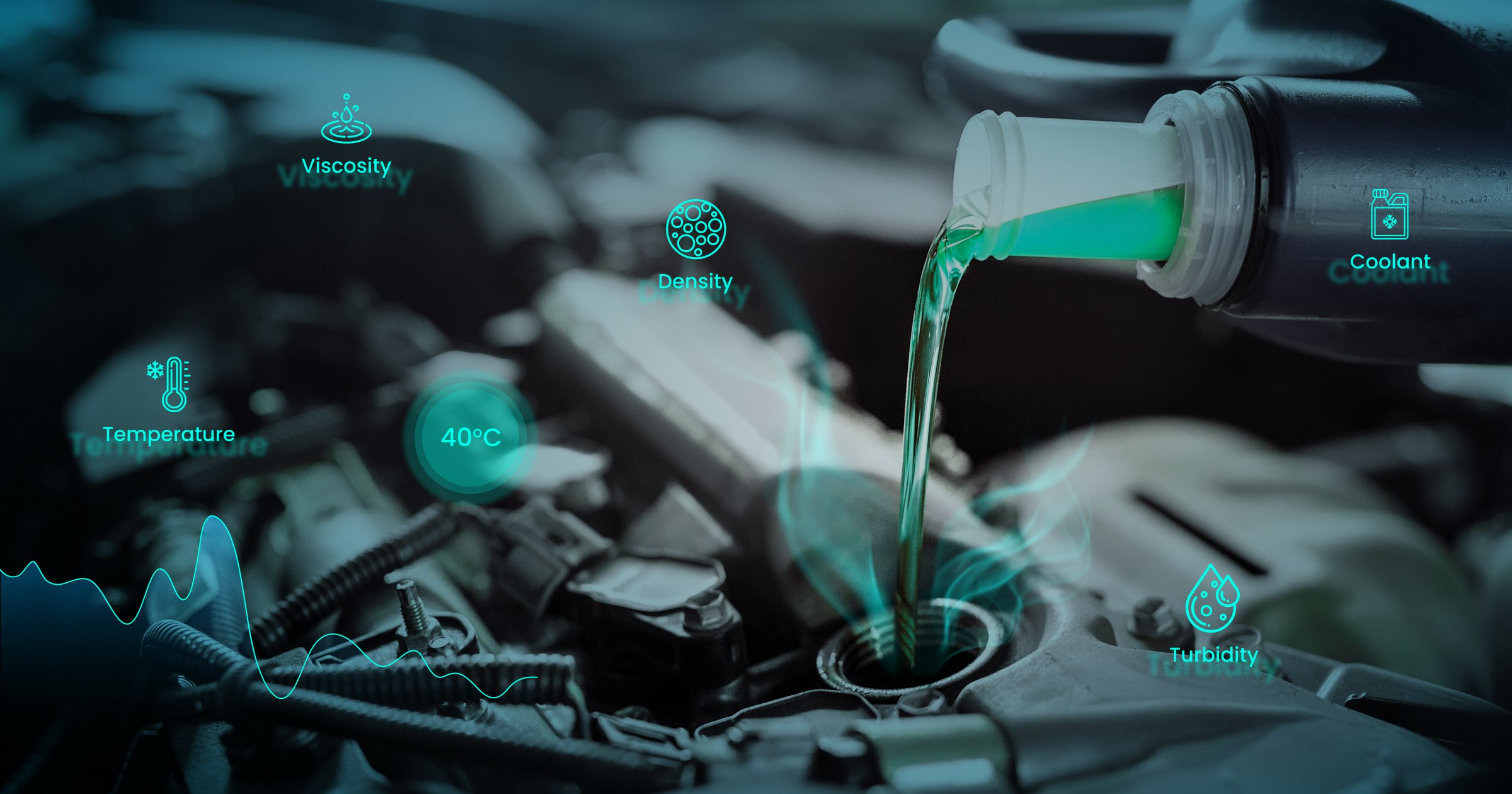
Coolant quality control: Top parameters to consider related to IoT in automotive
Optimizing the lifespan of cooling systems in various applications, such as automotive, industrial, and residential systems relies heavily on coolant quality control. Technicians and engineers assess several parameters to determine the quality of the coolants used in these systems, including:
- Density refers to the mass per unit volume of the coolant and affects both the heat transfer capacity and flow rate. A higher-density coolant may transfer heat more effectively. However, it can also increase resistance to flow and reduce overall cooling system efficiency.
Streamline Your Automotive Coolant Quality Assurance Through IoT!
Explore Solutions- Temperature is critical in cooling systems, affecting the heat transfer rate between the coolant and the heat source or sink. Controlling and monitoring coolant temperature within a specific range is essential for optimal cooling performance and system protection.
- Viscosity, or the coolant's resistance to flow, affects the cooling system efficiency by restricting coolant flow through narrow passages, reducing heat transfer efficiency, and increasing energy consumption.
Coolant quality control using IoT: The technology’s role
The Internet of Things, or IoT, is a network of interconnected physical devices, vehicles, buildings, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies, enabling them to collect and exchange data.
The potential role of IoT in coolant quality control is vast and has already been leveraged in many industries, including automotive, to improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and increase productivity. In coolant quality control, IoT enables real-time monitoring and control of various parameters, such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and coolant level.
By integrating sensors into coolant systems and transmitting data to a central system, manufacturers gain insight into the system's performance, identify potential problems, and take proactive measures to prevent failures.
For instance, IoT enables predictive maintenance, where data from sensors can be analyzed to predict when components may fail, allowing manufacturers to replace parts before they break down. This reduces downtime, increases productivity, and prevents costly repairs.
IoT can also enable remote monitoring and control of coolant systems, allowing manufacturers to monitor the system's performance remotely and make changes as needed. This improves the efficiency of coolant systems, reduces energy consumption, and prevents unnecessary wear and tear on components.
Furthermore, IoT integrates coolant quality control data with other systems, such as asset management and production planning systems, providing a holistic view of the production process. This gives insights into how coolant quality affects production output and quality.
IoT-Enabled Smart Water Purifiers: Clean and Healthy Drinking Water
Read nowMain challenges related to coolant quality in automotive
The quality of the coolant in a cooling system is crucial to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of the engine or other equipment. Several challenges related to coolant quality can arise, and addressing them is critical to prevent engine damage or failure. Here are some of the main challenges related to coolant quality in the automotive industry:
1. Temperature related:
- Overheating: One of the primary challenges related to coolant quality is overheating. If the coolant temperature is not maintained within the desired range, the engine overheats, which can cause damage or failure of engine components such as gaskets, pistons, or cylinder liners.
- Corrosion: Temperature fluctuations result in the corrosion of the engine block and other components. When the temperature is too high, it accelerates the corrosion process, bringing about premature engine failure.
- Viscosity: The viscosity of the coolant is affected by temperature fluctuations, enabling coolant expansion and contraction. This instigates the coolant to become too thick, restricting the flow and reducing cooling effectiveness.
2. Density related:
- Freezing: If the coolant density is too high, it induces coolant freezing. This is a concern in colder climates, where the coolant must be formulated to withstand low temperatures.
- Pumpability: The density of the coolant affects its pumpability. The coolant may not flow freely, reducing cooling effectiveness and potential engine damage if it is too dense.
3. Turbidity related:
- Reduced cooling capacity: Turbidity, or cloudiness, in the coolant is caused by the accumulation of contaminants and dirt in the system. This reduces the cooling capacity of the coolant, thereby increasing engine temperature and potential engine damage.
- Engine damage: Turbidity in the coolant causes damage to the engine, such as cylinder liner pitting, corrosion of bearings, and other forms of metal erosion.
4. Coolant level related:
If the coolant level is not monitored and maintained, it can result in the engine overheating, destabilizing engine components.
Enterprise-Class Top IoT Development Company
Contact NowSensors and solutions for coolant monitoring using IoT
In the last few years, IoT technology has gained prominence for maintaining the quality of engine coolant in automobiles. IoT systems provide real-time data on temperature, pressure, chemical composition, and usage, which helps prevent damage to the engine and optimize coolant usage. Here is a list of sensors and solutions that mainly help in coolant quality control:
1. IoT sensors
Many sensors come in handy to collect data on various aspects of the vehicle's performance, including coolant quality, fuel efficiency, and engine performance.
The Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) sensor, for instance, utilizes various electronic sensors to sense the condition of the engine oil during its operation. It provides accurate and real-time data on the oil condition, enabling the system to improve its interaction with the physical environment.
The LM35 temperature sensor, on the other hand, can be used in automobiles to measure the temperature of various components or fluids. For example, it determines the temperature of the engine coolant, transmission fluid, or intake air.
The level monitoring sensor monitors the level of coolant in the vehicle and alert maintenance teams when levels are getting low, or the tank is about to empty. In addition, the infrared sensor detects the coolant's impurities by analyzing the coolant's infrared radiation, notifying the relevant personnel to clean dirt and other contaminants in the coolant.
The ultrasonic sensor utilizes ultrasonic waves to determine the level of oil in the engine. Finally, a turbidity sensor is used for checking the cleanliness of the coolant, the air quality around the machine, and the humidity and temperature value in the vehicle.
2. Real-time multi-parameter coolant quality monitoring
Multi-parameter sensors used in real-time coolant quality monitoring allow for the simultaneous measurement of multiple parameters such as temperature, density, and turbidity. These sensors can be installed at various points in the coolant system, including the radiator, coolant tank, and engine block, to provide comprehensive system monitoring.
Temperature sensors, for instance, detect any changes in the temperature of the coolant, which is crucial in preventing the engine from overheating or freezing. On the other hand, density sensors ascertain any changes in the concentration of the coolant, which can affect the efficiency of heat transfer and flow rate.
Turbidity sensors identify any contaminants in the coolant that can cause corrosion or damage to the engine components. By continuously monitoring these parameters in real-time, any deviations or faults in the system can be detected early on, allowing corrective action. This can help prevent costly repairs and downtime for the vehicle or equipment.
3. Integration with maintenance systems
Doing so makes it possible to automatically generate work orders when specific parameters fall outside predefined limits. For example, if the temperature of the coolant exceeds a predefined limit, an alert can be sent to the maintenance system, which will automatically generate a work order to investigate and address the issue. This can help ensure that maintenance tasks are performed promptly, minimizing the risk of damage or failure to the engine or equipment.
4. Automated maintenance
An IoT solution automates many routine tasks in maintaining the coolant system. For example, automated sensors can monitor the coolant level and trigger a refill when it falls below a certain level. This ensures that the coolant is always at the correct level and reduces the risk of damage to the engine due to low coolant levels. Automated filtering systems remove contaminants from the coolant, ensuring it flows freely and efficiently. These maintenance tasks can be scheduled and managed automatically, freeing maintenance personnel to focus on more complex tasks.
5. Predictive alerts
Predictive alerts are generated based on the data gathered from the sensors monitoring the various parameters of the coolant system. As the sensors collect real-time data, they can identify any changes in the values of the monitored parameters that may indicate a potential issue or deviation from the desired values. This data is then analyzed using ML algorithms that detect patterns and anomalies. If a pattern indicates a potential fault or deviation, predictive alerts can be generated and sent to the maintenance team to fix problems before any serious damage to the vehicle occurs. These alerts are usually in the form of email notifications, text messages, or alarms triggered within the system.
IoT-Enabled Livestock Management: Revolutionizing Animal Tracking and Monitoring
Read nowOver to you
Modern vehicle engine systems are built using lighter materials and are required to operate at higher temperatures, which puts more strain on the coolant's performance and characteristics. The coolant must protect the engine against high temperatures and corrosion, be compatible with various engine materials, and lubricate the engine cooling pumps. If the coolant quality deteriorates prematurely, it can severely damage the engine and coolant systems.
IoT technology provides an opportunity to optimize coolant quality control, reduce maintenance costs, extend component lifespan, and enhance automobile operational availability. IntuThings offers a wide range of versatile IoT services that can benefit businesses of all kinds, helping you fully tap into the potential of IoT.
Book a Free 45-minute Consultation with Our IoT Experts Today! Get a customized roadmap and strategies to leverage IoT for coolant quality assurance for vehicles.